
What is SEO?
The practise of increasing your site’s organic traffic and rating on search engines like Google, Bing, and others is known as search engine optimization (SEO).
This includes developing high-quality content in addition to monitoring your site’s technical health, obtaining links from other sites to your site, maintaining your site’s local search visibility, and more.
How Do Search Engines Work?

To organise and rank content, search engines like Google use highly complex methods — or algorithms. Algorithms consider a variety of ranking parameters when determining how well a page ranks.
The long and short of it is that search engines collect digital content and organise it into pages of results. The ultimate goal is for searchers to be satisfied with the results they see in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Incorporating keywords into your content is a huge component of this. Keywords are words or phrases that people type into search engines while looking for anything.
Your page’s keywords should be relevant to your business and, preferably, have a high search traffic (i.e., enough people are asking a question on Google that you should write a corresponding page about it).
To uncover keywords that make sense for your approach, try tools like the Keyword Magic Tool or the Keyword Overview Tool.
Remember that repeating a keyword in a piece is an obsolete approach that will not help you rank in Google. Instead, utilise keywords to help you decide what to write about.
How Does Google Work?
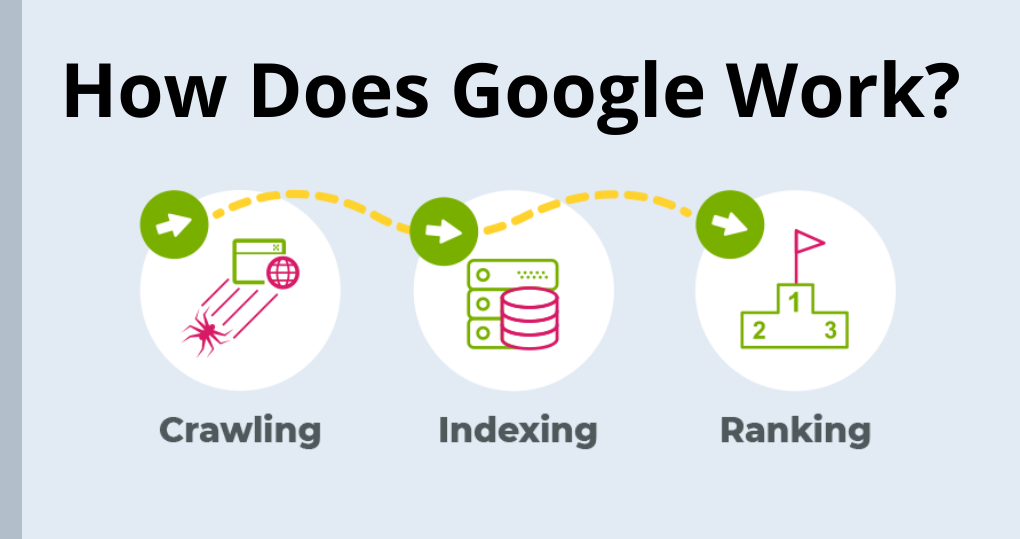
The fundamental goal of most SEO strategies is to achieve high Google rankings.
To identify and rank content, Google goes through the following steps:
- Crawling: Google uses “bots” to crawl the internet in search of new or updated pages. A page must have links going to it in order for Google to find it. In general, the more links pointing to a page, the easier it is for Google to find that page.
- Indexing: After then, Google analyses the URLs that the bots find and tries to figure out what the page is about. Content, pictures, and other media items will be examined by Google. The information is then saved in the Google Index (or its database).
- Serving: After evaluating URLs, Google determines which sites are most relevant to users’ search queries and organizes them in the SERPs accordingly.
Google Algorithm

Google’s internal mechanism for ranking content is referred to as the Google search algorithm. When it comes to ranking decisions, it considers a wide range of elements.
Unfortunately, no one outside of Google’s inner circle has access to all of the company’s ranking factors. It’s logical that Google would keep their secret formula so closely guarded.
Fortunately, Google provides best practises for consumers to follow. Experts such as John Mueller, a Google search advocate, also offer advise and answers on the algorithm on a regular basis.
That being said, here are a few things to keep in mind while optimising your site based on Google’s recommendations:
- Intent: Is your material answering your users’ questions or displaying what they want to see? Language, freshness, and synonyms all make a difference in this case.
- Relevance: Once Google’s algorithm has determined that your material satisfies the search intent of the query, it will scan its Google Index to see where your content sits in terms of relevancy. On-page SEO is critical in this case. If you provide the clearest and most relevant material to searchers, you will most certainly rank better in the SERPs.
- Quality: It may appear that information with a high level of search intent and relevance is already of high quality. However, the truth is that the Google Algorithm considers quality. E-A-T — expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness — is how many people refer to this evaluation.
Google Penalties

Google penalties are unfavourable outcomes or effects that have an impact on a website’s ranking. These are manual actions made by Google in response to unethical SEO techniques. Here’s a quick guide to avoiding the blunders that result in these fines.
Learning the ins and outs of the SERPs can be difficult; have a look at the following thread on SEO myths to understand how to recognise false SEO advice from a mile away.
Why Is SEO Important?

SEO is vital since it improves your company’s online presence.
Paid advertising and social media can also help with visibility, but the beauty of SEO is that if done effectively, it can continue to deliver traffic over time.
As a result, SEO provides “free” visitors to your website. High-quality pages that answer a user’s query can appear at the top of the SERPs if you publish them. This is a wonderful spot for searchers to become comfortable with your website and business.
There are, however, other reasons to prioritise SEO. It may be able to:
- Bring converters with you.
- Obtain more leads for you
- Sales should be encouraged.
How Does SEO Work + Examples

SEO is the art and science of persuading search engines to promote your information as the best, most authoritative, and most thorough answer to their problem to their users.
As previously stated, Google bots collect information about pages and add it to the Google Index. The index is then reviewed by search engine algorithms, which utilise hundreds of ranking factors to determine where pages should show in search engine results pages (SERPs) depending on user queries.
A typical SERP displays paid results first, followed by organic traffic (which is traffic based on the quality of pages).
On-Page SEO

On-page SEO is the process of optimising the content of a web page. Unlike off-page methods (which we’ll discuss next), you have control over these variables.
You can edit title tags and meta descriptions on your own website, for example, and write your own content.
On-page SEO elements can also include the following:
- Keywords: Begin your content development process by using a tool like the Keyword Magic Tool to conduct keyword research. You may get statistics on how many people search for a specific term, as well as a prediction of how difficult it will be to rank for it. This will assist you in deciding which keywords to target in your article.
- Content Creation: After you’ve decided on primary and secondary keywords for a topic, start writing content with the user in mind. This entails figuring out what people looking for a specific phrase are looking for. If someone searches for “Honda Pilot colours,” make sure to provide the colours as well as any accompanying photos that the consumer would wish to see.
- Page speed: Users will frequently leave a page if they do not receive the information they require immediately. Using Google’s PageSpeed Insight tool, make sure your page is quick enough. If there are any problems, the tool will provide you suggestions for how to fix them.
- Internal linking: Because Google scans the internet via links, internal linking is a critical component of SEO. Links are considered as a vote of confidence; take advantage of this by linking from high-authority pages to new or under-performing pages.
Off-Page SEO

Off-page SEO refers to all of the optimization techniques used outside of your own web properties. These off-page strategies aid search engines and users in determining whether or not your website is authoritative, relevant, and trustworthy.
While social media and influencer marketing are significant aspects of off-page SEO, link development is likely the most crucial.
The activity of obtaining other websites to link to your website is known as link building. Links operate as votes of confidence, thus having a backlink from a high-authority site can bring your site additional visitors as well as enhance its authority.
Remember that more links aren’t always better; spammy backlinks will have a negative influence on your site and may even result in penalties. To avoid this, avoid buying links or taking shortcuts.
Link building is challenging, but the payoff in terms of traffic, brand recognition, and authority can be substantial.
We’ll go over link building in more detail later. First, let’s go over the ins and outs of the major SEO topics.
Content
“Content is king,” as Bill Gates once said. That is still the case.
What does this mean in terms of SEO for you? The better the content, the higher you’ll rank in the SERPs.
But how can you tell the difference between good and exceptional content? We’ll get into that in this part, but first, let’s go over some key content focus areas.
Meta Titles and Meta Descriptions
In many cases, what Google shows its users in the search results is determined by these areas of a page.
In many cases, what Google shows its consumers in the search results is determined by these portions of a page.
It’s crucial to have an accurate meta title (also known as a title tag) that clearly describes what the page’s content offers to the user – it’s the reason they click on your result or not.
Meta titles and meta descriptions are essentially sales text that entices users to visit a page while also assisting Google in better understanding the content and purpose of that page. Include your major keyword in your meta description because it is beneficial to both users and search engines.
Headings
The title that users view when they first arrive on your page is an important indication to Google. It, like the meta title, must be clear and incorporate the terms that the user looked for. This is yet another essential indication to Google, as well as reassuring to the user.
Writing Style
Keep your writing clear, straightforward, and focused. Maintain brevity in your words, divide your content into reasonable sections, and stay on subject. This allows readers to get right to the point of their problem’s solution. Organize your information such that the value it offers is obvious, understandable, and engaging.
Rich Content
When possible, use rich media like music, video, and illustrative graphics. However, keep in mind that Google is unable to comprehend the content of images or videos.
So, when you do include these richer formats, make sure they’re accompanied by the right meta tags to help Google and others with visual impairments comprehend what they’re looking at. You might also include a written version for users that like that type of content.
Outbound Links
Outbound links, also known as external links, refer to sources that verify the accuracy of your material and establish your and the author’s credibility.
Authorship
Where possible, include the author’s name in the text. If they are authoritative, the content will gain credibility.
Keep in mind, though, that your material does not exist in a vacuum. Each piece of content must be viewed as part of a larger, more cohesive content strategy. You’re thinking in terms of content marketing as soon as you do that.
Types of Content
Different sorts of content are suited for different users and phases in the funnel. A good content strategy will include a variety of formats, such as:
- Lists: Lists are popular among both humans and Google. They’re simple to skim and interact with.
- How-to guides: How-to guides are ideal for delivering a step-by-step solution to a search query. Long-tail keywords are those that the user uses to ask a precise query.
- Long-form guides: These might be time-consuming to create, but they can help your audience grasp a single or broad topic in greater depth.
- Tables: Google can easily read tables of data or information on your pages. They’re also useful for your audience when they need to process information on a particular issue.
- Graphics: Images, pictures, and illustrations are examples of graphics. Google is increasingly incorporating these in the SERPs, particularly on mobile. Plus, when used correctly and categorised, photographs can drive traffic from Google’s image search, which is very popular with certain industries and sorts of inquiries (i.e., fashion or travel).
- Infographics: Infographics are visuals that contain information (typically illustrations and text), allowing them to function as stand-alone content. They’re excellent content to share with your audience on social media in order to increase interaction. They’re also a fantastic technique to create links.
- Videos: Google is increasingly adding videos in its search results. This is especially true of instructional DVDs.
- Podcasts: Podcasts have been increasingly popular in recent years, particularly in specialised markets. Google displays them in the usual search results, much like movies and photos.
- Webinars: A webinar is a live online meeting or presentation that is available to the general public. Webinars are wonderful for not just engaging and growing your audience, but also for providing long-term content. This is because you can broadcast the live event on YouTube as a video that people can watch at any time.
- Ebooks: Ebooks are digital books, mainly in PDF format, that companies frequently distribute for free. They’re ideal for in-depth content that’s too extensive for an article, and they may also be utilised to learn more about your target readers.
3 Tips for Creating Better SEO Content
- Starting with some in-depth competitor research is always a good idea. What do your immediate competitors have to say about you on their blogs? What are the keywords they’re aiming for? You’ll want to look for ways to go into further information and depth concerning those topics, as well as content gaps where you can differentiate yourself from the competition.
- The length isn’t the be-all and end-all. Have you noticed how blogs that target a specific keyword are shorter? Use as many words as you need to get your message through if you believe longer content will benefit your audience. However, keep in mind that many readers are spending less and less time reading internet publications.
- When writing, keep accessibility in mind. You may use tools like the SEO Writing Assistant to assist you figure out your content’s tone and readability.
Now that you’ve learned the fundamentals, check out the following Twitter thread for content strategy advice.
Technical SEO

The quality of your site’s infrastructure and usability are at the heart of technical SEO. Good technical SEO ensures that Google finds your content (when you want it to) and accurately assesses and indexes the data it finds.
What Are the Top Priorities for Technical SEO?
- Page Speed: Every page must load quickly. Google intends to offer quicker pages a higher priority to its consumers since they provide a better user experience.
- Mobile-friendliness: Users must be able to conveniently consume your content on their mobile devices. Because Google rates your content based on how well it performs on mobile devices, it’s critical that you get this right.
- User interface: Google wants to promote sites that are appealing to consumers in terms of design and usability. Your site layout must ensure that when a person arrives on your page, they find it appealing, understand what it offers, and are aware of the navigational options available to them.
- Schema markup: Schema markup is a markup language that is similar to Google’s native language. Schema markup describes your information to Google in a way that it can understand, making it simple to consume.
3 Tips for Better Technical SEO
- Check Google’s index for duplicate versions of your site.
- Pay strict attention to site speed – look into anything that is slowing down your page’s performance, and be aware of any technical elements that may slow it down. Google PageSpeed is a free tool that lets you see how well your web pages perform in terms of performance.
- Don’t forget to include a robot.txt file in your directory.
Interested in learning more about how technical SEO works in practise? Take a peek at this Twitter conversation with Schema App’s CEO and co-founder
Website Architecture
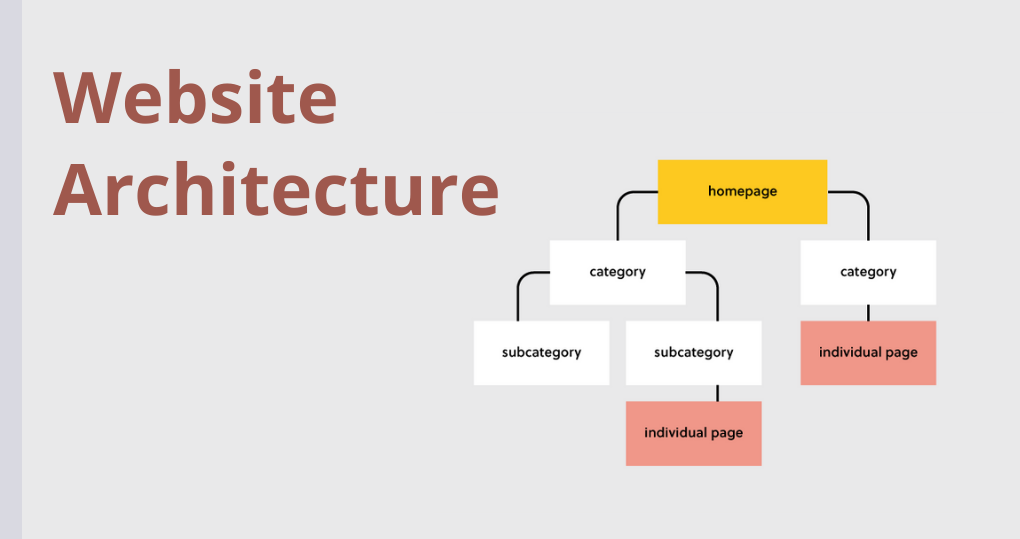
The way web pages are collected and organised is referred to as website architecture. The user’s experience is prioritised in great website architecture. Users are more likely to spend more time on and engage with a website that is easy to navigate and has good architecture.
When it comes to a website’s user experience, it’s critical to make it as easy as possible for visitors to reach where they want to go with as few clicks as feasible. They should also be able to get from point A to point B and back to point A with ease. Sites with good structure are also easier for Google to crawl and index.
3 Tips for an Organized Website Architecture
- Make your URLs as simple as possible. Google prefers clear, simple URLs. Simple sentences, lower-case letters, hyphens between words, and words that explain the page’s content are all good choices.
- The use of a site map aids Google’s crawling of a website. There are a few options, but the XML site map is the most common.
- Be wary of keyword cannibalism. Check out our post on keyword cannibalization to learn more about how to avoid it.
Authority and Trust

Google considers authority and trust in a variety of ways. E-A-T. and YMYL. are two typical abbreviations for these metrics (Your Money or Your Life). Let’s look at both of them.
E-A-T
The abbreviation E-A-T — Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness — is used by Google to refer to overall credibility. They evaluate E-A-T (credibility) on three levels: the page, the author, and the website. They’re also looking to see if the content is legitimate in terms of the answer it claims to offer.
The words “expert,” “authority,” and “trust” (or variants) appear more than 200 times in Google’s guidelines.
Let’s examine briefly at each component of E-A-T.
- Expertise: Is the information correct? Expertise Is the information accurate? Is it appropriate for this author or brand to write about this subject?
- Authoritativeness: Is the author regarded as authoritative in their field? Is the company’s name well-known in the industry? Is the information linked to from other authoritative websites, brands, and individuals?
- Trustworthiness: Is the content trustworthy, and does the brand and the writer have a solid reputation?
Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) Pages
Quality raters use the acronym YMYL, which stands for “your money or your life.” This word refers to pages or themes that “may potentially influence a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety,” according to Google’s standards.
As a result, the pages that display YMYL themes must be authoritative and trustworthy. Here’s a list of some of them:
- Current events and news
- Finance and the government
- Safety and health
- Groups of people with similar identities
- Health and Fitness Education
- Housing and job opportunities
Because low-quality YMYL content might directly impair users’ well-being, Google claims to have “extremely high Page Quality requirements” for such pages.
When creating web content, using both E-A-T and YMYL can help you obtain better ranking results. Finally, you’ll want to give users the best content options possible so that they return to your site with other similar questions and concerns.
3 Tips for Building Authority and Trust
- Set aside a page on your website (the most common choice is “About Us”) to highlight your brand when it appears in significant magazines.
- Use schema markup on your website to provide Google with more content information.
- Showcase consumer reviews and ratings on a page on your website.
Link Building

The activity of obtaining other websites to link to your website via hyperlinks is known as link building. Backlinks are effectively votes of confidence or authority from other sites, and they are one of the most crucial parts of SEO.
The more high-quality referring domains your website has, the more trustworthy it seems to Google.
Why Link Building Is Important
Obtaining backlinks is another excellent technique to improve your page’s ranking in the SERPs (provided these backlinks are coming from reputable websites).
Internal inbound links — that is, links from your website directing to other pages on your website — are also recommended. This aids Google’s navigation of your site and indicates the importance of the pages you’re pointing to.
Penguin was a basic algorithm change introduced by Google in 2012 to assist combat “link cheating” (meaning to prevent sites with spammy link profiles from ranking high).
They announced in 2017 that the process of recognising and ignoring spammy links is now done in real time. This means that low-quality backlinks will be ignored and won’t help you rank.
When it comes to link building, focus on quality rather than number.
How to Build Links
Creating content that will naturally generate links is an excellent strategy to start creating a backlink profile. Here are a few ideas:
Creating niche-specific material that is both valuable and authoritative
Choosing the proper keywords to target, i.e. sending your material to the right audience
Including assets that can be linked to, such as infographics
However, link development isn’t always so simple – actively launching a link-building campaign can improve that process.
Connect building entails finding people who can link to your content (website owners, journalists, bloggers, and so on), alerting them to it, and persuading them to link to it from a relevant page on their site. Isn’t it straightforward?
It’s not only simple, but it’s also time-consuming. The following are the essential steps to starting a link-building campaign:
- Find the appropriate publishers: Finding the right publishers is one of the more time-consuming aspects of the process. You’ll want to look for credible publishers in your business or specialty (bloggers, news outlets, etc.). Using our Link Building tool, you may create a list. It’s especially useful to know where your competitors’ work appears.
- Draft a pitch: You’ll need to prepare a pitch to send to the publishers you’ve chosen. This pitch should be professional, personable, and natural-sounding (in other words, avoid being overly gimmicky). Introduce yourself and explain why your content is relevant to them and their readers.
- Send your emails to publishers: After that, you’ll need to send your pitch. You may achieve this by using our link-building tool and keeping track of your correspondence with publishers. You’ll want to make sure you’re answering any message you receive in a very timely method.
- Do link management and upkeep: Keeping the links you’ve earned updated is one of the simplest strategies to sustain your visibility (not broken). You can achieve this by using our Link Building tool. You may also utilise the Link Building tool to find publishers who are already linking to your page with no-follow links and contact them to request that they follow your page.
5 Tips for Creating Engaging Content That Earns Links
- Create pieces using data: Create content that includes original data, as well as unique and helpful (or interesting) data analysis.
- Be emotional: Make content that appeals to people’s emotions: Content that appeals to people’s emotions is excellent for gaining links.
- Be humorous: If you can hit the perfect note with your humour and it resonates with your audience, this form of material is a surefire way to get links. It’s also wonderful for generating buzz and increasing brand awareness on social media
- Focus on collaborations: Create content that incorporates quotes or interviews from industry influencers or leaders, with a focus on cooperation. Because you’re associating your business with a well-known and relevant industry leader, this form of content will have authority built in. With this type of content, you’ll almost certainly have one link right away – from the party with whom you partnered!
- Aim to craft authoritative pieces: Creating authoritative material is difficult, but it pays off when done well. When your material extensively and accurately covers a topic, it adds value to the target audience and makes it easier to obtain links.
For some practical advice on link building, check out this Twitter conversation.
Local SEO

Local SEO is a set of strategies for optimising a company’s online presence for local search inquiries. For example, if you searched on Google for “auto dealers near me,” you were using a location-specific search query.
The “map pack,” or “local pack,” is made up of three elements that are returned in response to location-specific queries:
- Results from Google Maps
- Local business outcomes
- Results from a natural search
The following is an example of how the results will appear:
Google Business Profile

The above data is influenced by Google Business Profiles, or GBPs, for businesses (formerly Google My Business).
Google Business Profile is a tool that gives firms in the SERPs high-visibility branding.
Prospective consumers can reach you using your GBP in a growing variety of ways. Using your GBP page to boost your local SEO efforts is a smart idea.
GBP evaluates content based on three basic criteria:
- Relevance: Is your company relevant to a searcher’s location-specific query?
- Distance: Using the search criteria, Google estimates the distance between each relevant result. If a searcher chooses not to provide much information about their specific location, Google will use whatever information they have to provide the best result.
- Prominence: The prominence of a company refers to how well it is known. It’s also dependent on how much information about the company is available online.
3 Tips for Improving Your Local SEO
- On your Google Business Profile, include as much information as possible about your company and its operation hours. People are more inclined to be repeat consumers if they receive accurate information about your company.
- Make sure your GMB page has the correct category (and any applicable subcategories) for your business. This ensures that your company’s relevance to users’ search queries is suitable.
- Examine what your competitors are up to. What can you do to improve your company’s performance?
Here are some more pointers for ranking high in the local SERPs.
Social Media

It may come as a shock, but using social media is an important part of best SEO practises. Social media doesn’t directly effect results, but it is a critical off-page SEO tool that helps businesses obtain exposure, amplifies material for possible backlinks, and helps develop brand awareness in your market.
Some organisations, for example, use social media platforms like Instagram to highlight their work culture and promptly and directly respond to client enquiries about items (or handle concerns).
When used effectively, these platforms may help manage brand reputation and organic shares. Again, it won’t have a direct impact on your website’s position, but the exposure may lead to backlink chances, which can help your site rank higher in the SERPs.
3 Tips for Leverage Social Media in SEO
- LinkedIn is a fantastic tool for sharing professional stuff with your network. This is a wonderful platform to remain updated with all of your pertinent information if you want to engage your audience and display thought leadership.
- Share any exciting business news on social media. The more authoritative content you publish across social media networks, the more likely it is to be featured.
- Using social network share buttons on your website, as previously discussed, is a terrific idea. This on-page optimization encourages visitors to share your material, and it can help you build backlinks.
In the thread below, you can learn more about how to avoid standing out on social media.
F.A.Q.
How Fast Does SEO Work?
Search engine optimization is a method that should be implemented over time. You must develop a holistic SEO approach that includes both on-page and off-page optimization for your strategy to produce fruit.
After implementation, some of your efforts will pay off in the short term. Changing meta names and headers, or upgrading the content on a few pages, are two common examples.
Other initiatives, like as using Schema markup on pages, producing a large volume of interesting material, establishing authoritative links, and generating favourable reviews, require time and pay off over time.
How Do I Rank #1 in Google?
No single element will alter the performance of your SEO campaign. All of the elements mentioned above operate together, and it is the sum of all the signals Google receives that causes the needle to shift in your favour.
Your best hope is to build a content strategy around the proper keywords, produce consistent material, optimise for local and technical SEO, and pivot your plan as needed based on results.
What Are Some Examples of SEO?
In addition to the technical aspects of website optimization, a complete SEO plan includes competition analysis, content production, and content amplification. The following are examples of good SEO:
- Creating a blog post based on keyword research
- Optimizing current content to increase the likelihood of your webpage being used as a featured snippet in the SERPs
- Working on technical SEO features to increase website speed, as well as a variety of other things
Check out this article on the latest SEO trends for some helpful suggestions and trends that demonstrate how versatile SEO can be.
How Do I Learn SEO?
You may study SEO for your business in a variety of ways. If you’ve opted to take on SEO on your own, your approach and learning style become even more crucial.
There are free school classes that grant certifications, and Google itself offers Google Analytics training and certifications, which is very beneficial if you plan to track the success of your site.
Some firms are unable to scale rapidly or efficiently enough to understand and apply SEO on their own. In this instance, employing an SEO service might be one of the less stressful ways to ensure that your business receives the attention it needs.
For additional information on breaking into the SEO business, check out some of our Twitter tips.
Conclusion
Don’t be intimidated by the vast amount of SEO material available. Professionals with varying levels of SEO experience can find a way forward with us. SEO is an art and a technique that takes time to master, and the world of search engines is always changing.
To study SEO, all you need is a curious mind and a desire to assist searchers in finding the information they want.
Would you like to learn more about SEO? Take a look at these ten advanced SEO methods.
Do you want to view some interesting SEO content? Take a look at our series of webinars on how to develop a winning SEO strategy.
